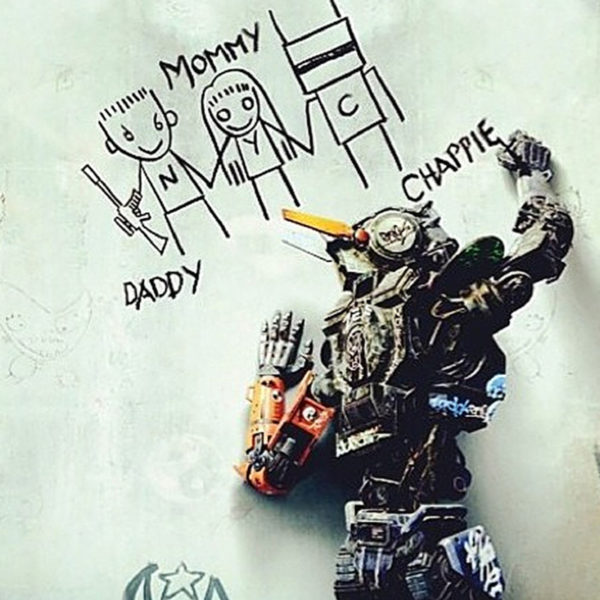
. . . In other words, Chappie can be read as an allegory that calls for us to recognize our ill-treatment of the other, and the film seeks an alternative ethic that does not recourse immediately or uncritically to fear or hostility, leading to violence. We are to be more embracing of the ‘other’ who is, ultimately, more complex than we might first assume, and is never entirely ‘other’.
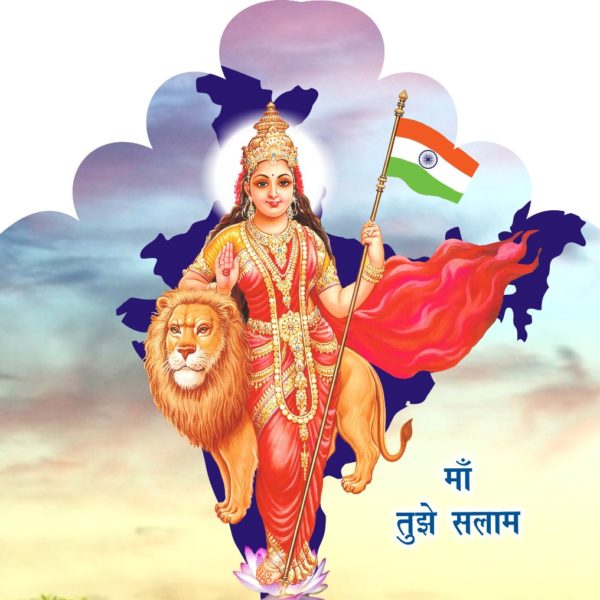

In May 2014, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi travelled to the riverside holy city of Varanasi to worship mother goddess Ganges in gratitude for his victory in the national elections. This grand self-promotional gesture by a prominent Hindu nationalist politician illustrates how religion and politics remain enmeshed in India. Even though the democratic constitution of the nation-state has been modeled on western varieties of secularism, everyday politics is infused with religious iconographies.

The biblical images of God as divine king are often handled with embarrassment in a more egalitarian age. However, although it may appear little more than accommodation to ancient despotic assumptions, throughout the Scriptures the kingship of God is presented as a great force for liberation against all human tyrants.

When Paul Tillich’s Theology of Culture hit the shelves of the Anglosphere in 1959, the book seemed to go against the prevailing mood of the time. Wages and living-standards across North America were up as the post-war ‘Keynesian miracle’ took its full effect. While the previous year had seen economic contraction in U.S. output, it was to be a small pause in a seemingly unstoppable advance. Canada and Australia also rode high in the economic league-tables, as the administrations in Ottawa and Canberra saw conditions of near full-employment.