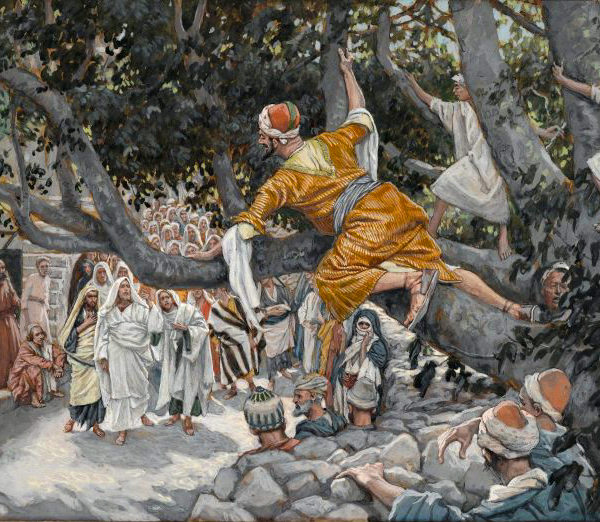
In the declamation of Isaiah 1, the prophet associates Judah and its rulers with Sodom, for their inhospitality, injustice, and the presumption that they can hide this from God. Zacchaeus, a man characterized by such Sodom-like injustice, is delivered from this as justice is welcomed into his house in the person of Jesus.

The Parable of the Pharisee and the tax collector is situated against the backdrop of the promise of the coming kingdom and the vindication of the righteous that will come with it. We too can look for future vindication and Jesus’ parable may speak to our own convictions about being on the ‘right side of history’.