Sometimes it makes sense to concentrate on a single concept in order to understand the contribution of an individual to the history of ideas. This may mean artificially reducing the complexity of a person’s thought and vision. It may, however, be helpful in finding a hermeneutic ‘entry door’ into those thoughts and visions.
I have come to the (preliminary) conclusion that “Decentering” is such a key concept in the writing of Rowan Williams. “Decentering” features in Williams’ work both on questions of individual spirituality and matters of collective well-being. In Williams’ approach the individual and collective dimensions are not to be viewed separately but together. Individual choices bear upon the order of state and society and collective decisions provide the framework for the welfare of individuals and their ‘pursuit of happiness’.

The Israelites no longer needed God to provide manna for nourishment, but had their own land. The manna, in one sense, represents charity work. It is helpful and gives immediate attention to the person in need. Yet, if we are not advocating for the Promise Land where housing is affordable, jobs are of plenty, oppression is repressed, etc, then we need to have a reality check.
In a recent piece about Les Misérables, which is in general a fine study of the dynamics of law and grace in the film, Michael W. Hannon worries that a view of the state, and the political realm more broadly, as an unnatural institution is insufficient for a vibrant and vigorous engagement of this realm, or as he puts it “our faith in law.” Hannon aptly notes that Valjean, one for whom “it seemed as though he had for a soul the book of the natural law,” is the ideal in Hugo’s work. Valjean’s remarkable conversion, for instance, results in a situation in which he recognizes a greater sense of moral obligation rather than less.

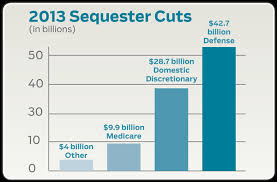
In the interest of full disclosure I’ll note at the outset that I am married to a federal government employee. The idiotic faux crisis of the sequester, like its recent precedents, is personal in our household. I read the end of the gospel passage for this week and think, “hell, they’ve put plenty of manure around this fig tree of Washington politics and it hasn’t produced fruit for years. Let’s cut the damned thing down.”