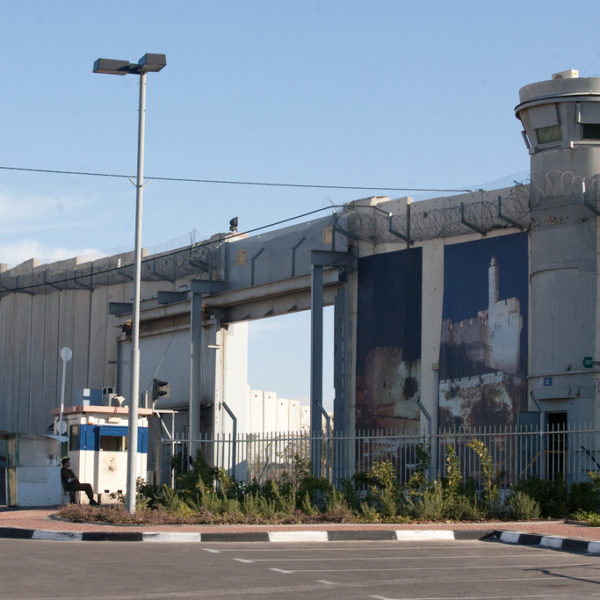
I wish to thank Dr. Bernstein for his thoughtful and irenic response to “Zionism Unsettled” (hereafter, ZU). . . . ZU is indeed a hard-hitting document. It says things many people would rather not have discussed and calls out both Jewish and Christian Zionists for their contribution to the misery and suffering of the Palestinian people. Such a resource, which could be utilized at the congregational level, was sorely needed. The Israeli occupation began in 1967, when I was four years old. I’m now a grandfather, and yet it still continues.

As I compose this, the gloves are being taken off on all sides, and in every direction, over the matter of the Presbyterian Church USA’s 310-303 approval of divesting from three companies (Caterpillar, Motorola Solutions, and Hewlett-Packard) whose business with Israel are seen to impact the Israeli occupation of Palestinian territories.

What political theologies are embedded in and shape Zionist and Palestinian refugee mappings of space and place? This is the animating question of my new book, Mapping Exile and Return, which stems from my doctoral studies in theology at the University of Chicago and 11 years of work in the Middle East.
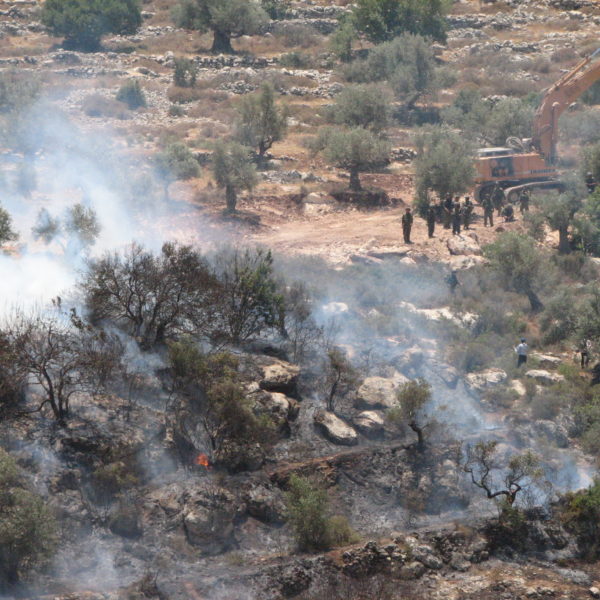

In 2008, I worked in Ramallah as a journalist and interim editor for the Palestine Monitor, a web-based news source committed to “exposing life under occupation.” I traveled throughout the West Bank, writing several articles about the village of Ni’lin, whose olive groves and roads are fractured due to the construction of the separation wall.

n the matter of U.S. support for Israel, religion and politics operate as Tweedle Dum and Tweedle Dee, reinforcing each other in a slapstick display of tomfoolery. Although presidents have for decades lodged verbal objections to settlement expansion in the Palestinian territories, the Congress continues to authorize 3.2 billion dollars per year for Israel while Christian Zionist organizations send tax-exempt millions directly to the settlements.
Hope is not drawn from the world-that-is. Hope is grounded in perceptions of the world-that-ought-to-be. It arises from the power of the world-that-ought-to-be. For Christians, the world-that-ought-to-be is the eschatological Kingdom of God. It is expected in the future, in God’s time. But, it is also in the present, which is God’s time. The Kingdom is a perpetual possibility, even as its realization must be perpetually deferred in its fullness.
When the Committee on Middle East Peace finally made its motion to divest–you guessed it– a substitute motion was made, not divest but rather to invest in the Occupied West Bank. This was a masterstroke of polity, but a completely ridiculous proposal of policy. Presbyterians suffer from congenital niceness, which is the main reason that it had taken us eight years even to get to the point where we could make the least confrontational action possible on the issue, selling our own stocks and bonds.
In the case of Iran, deterrence looks less like realism and more like nostalgia for another era. The limits of nuclear deterrence push us to reconsider how to limit war and act responsibly in a world given to episodes of madness….