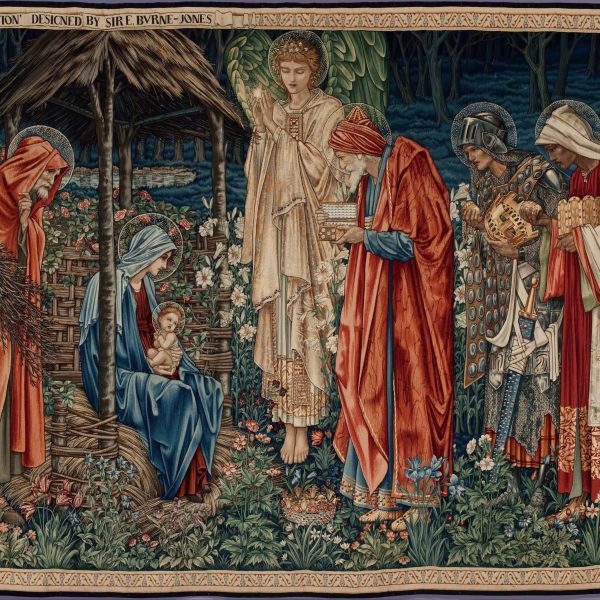
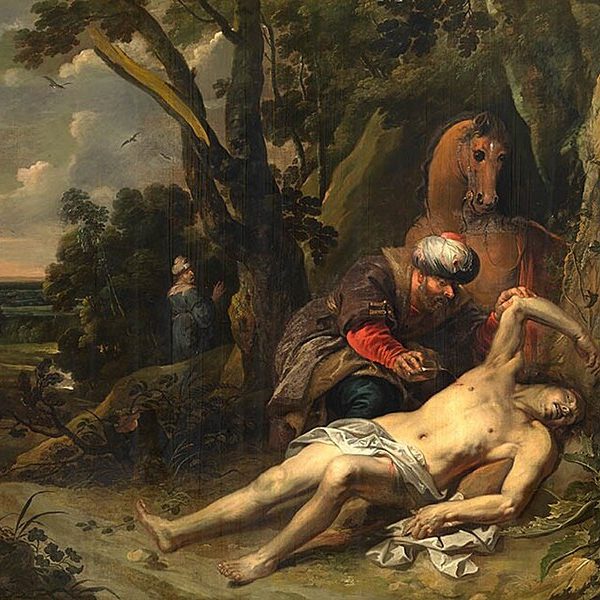
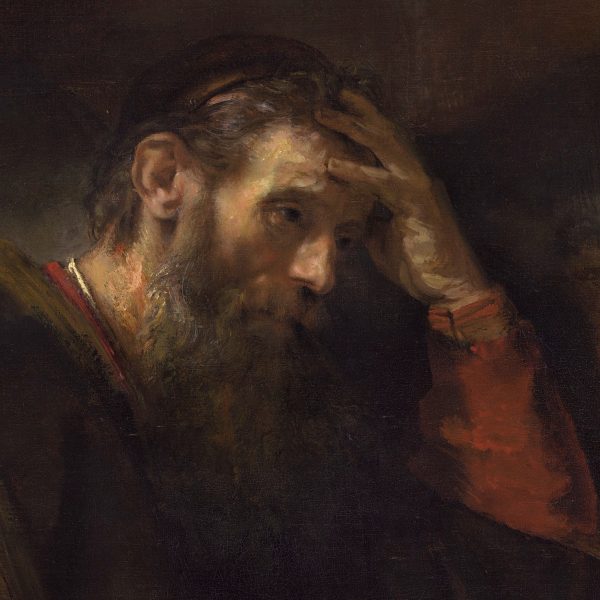
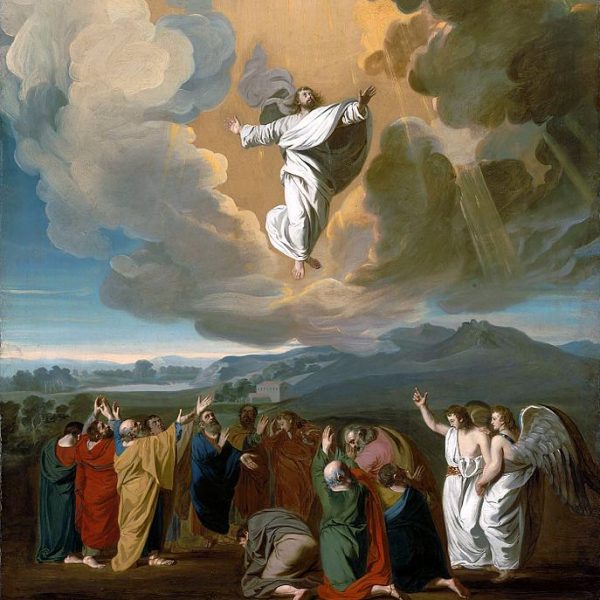
Amy Lindeman Allen
Amy Lindeman Allen is Indiana Christian Church Associate Professor of New Testament at Christian Theological Seminary. She is an ordained minister in the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America and has authored For Theirs is the Kingdom: Inclusion and Participation of Children in the Gospel according to Luke (Lexington/Fortress: 2019, 2023) and The Gifts They Bring: How Children in the Gospels Can Shape Inclusive Ministry (Westminster John Knox, 2023).Essays

The author of 2 Peter maintains that in order to wait well one must place trust in God and God’s promises (3:13). What sets a follower of Christ apart in the communities to which this epistle is addressed is that they do not act according to their own interests, or even their own timeline, but rather, in accordance with the promise of God.

In the midst of a complicated and troubled world it may seem impossible to make a difference, and yet, the wish of a little Israelite girl says otherwise. The spirit of the young Israelite girl and her larger cadre of enslave servants to Naaman live on today in the resourceful actions and tireless work of so many influential youth in our world, those whose passion and will for change persist.

Jesus and his disciples can be seen to both affirm and expand the construction of first-century family, even as they are not limited by it. Such a reading of Mark complicates any single definition of “biblical family” in favor of recognizing the fluid and constructed nature of family systems across time.

For those who are most vulnerable today—those at risk of infection due to socio-economic injustices that put them in greater harm’s way and/or age and immune-deficiencies that leave their bodies more compromised to the most severe effects of the COVID-19 virus, particularly in the United States, the disproportionate numbers of people of color whose communities are being ravaged by this disease—John’s text speaks a word of encouragement and hope.

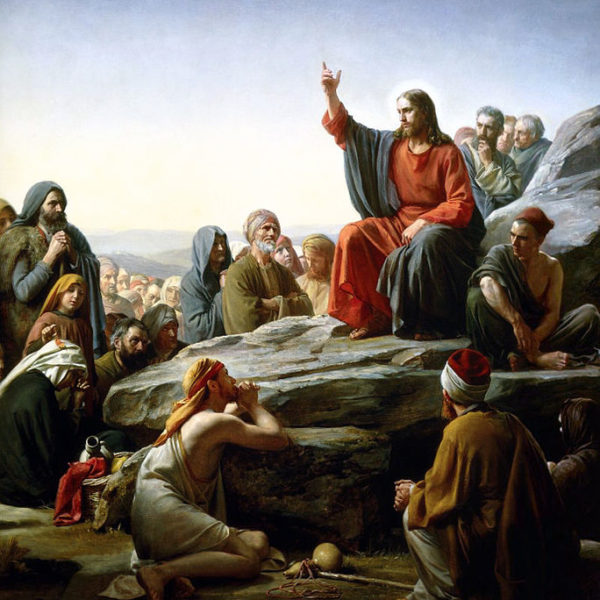
The trouble in American Evangelicalism and in Christianity more broadly, is that standing face-to-face with our Messiah, we find ourselves at a loss of how to serve. What does it mean to be a follower of Jesus? What, beyond the instinctive sense that we are to follow Christ, does it mean to follow? What are we looking for?

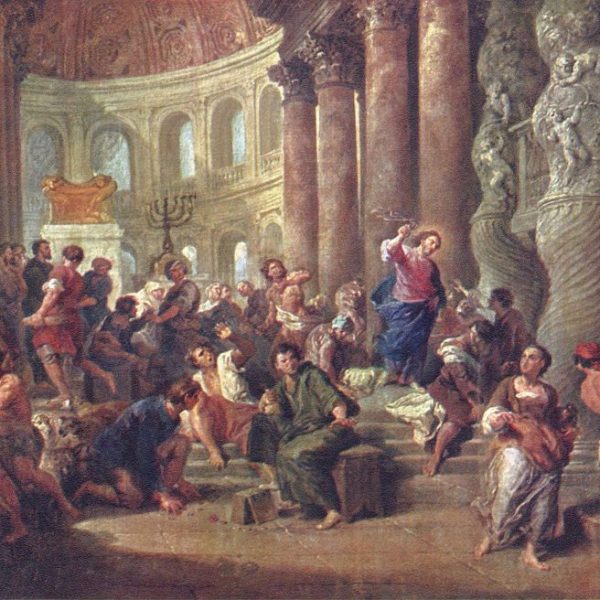
Jesus does not command those with privilege to make space at their tables, to give a portion of their excess to charities, or to invite a disadvantaged neighbor to join the feast. No, Jesus invites those with privilege to put off their privilege, and then to use the excess that their privilege has still provided to feed not their fellow privileged friends, but those who are most in need.

In the midst of a complicated and troubled world it may seem impossible to make a difference, and yet, the wish of a little Israelite girl says otherwise. The spirit of the young Israelite girl and her larger cadre of enslave servants to Naaman live on today in the resourceful actions and tireless work of so many influential youth in our world, those whose passion and will for change persist.

The Pharisees were not wrong to question Jesus, but as much as we might want to empathize with them, to agree that there are simply certain things good people do not do, Jesus rejects human propriety as an orienting standard. Jesus is talking about the human heart, something Christians today also must consider.
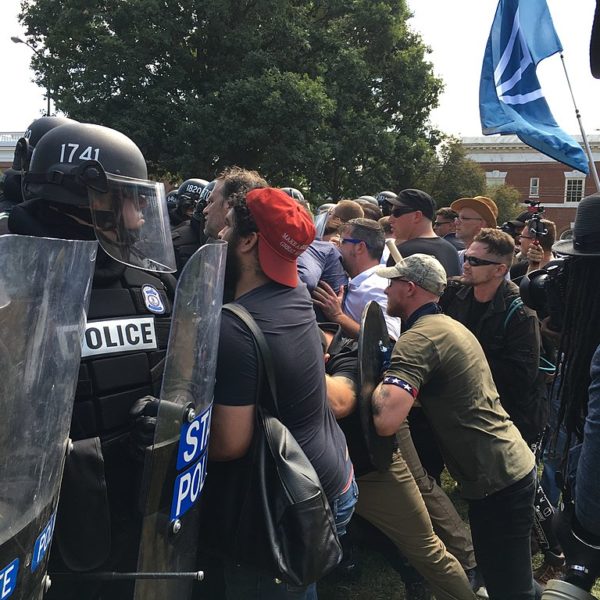

Christians are called not to ignore despair, but to help sow joy in its wake; not to condone hate, but to be all the more zealous in their own loving in its face. The politics of overcoming evil are about neither ignoring nor condoning evil, but rather, fighting it with the strongest power possible—love.
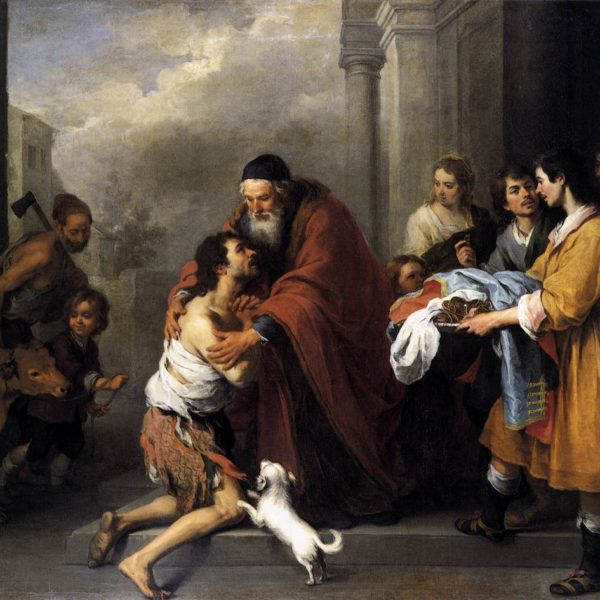

Although the parable is typically referred to as that of ‘the Prodigal Son’, the son who receives the father’s welcome has long since fallen from his state of prodigal living into one of the most abject poverty and lack. This father’s loving embrace challenges us to consider our provision of welfare and welcome to those in need among us, irrespective of how ‘deserving’ we might suppose them to be.

‘And this is my prayer, that your love may overflow more and more with knowledge and full insight.’ The notion of love overflowing in knowledge is odd to modern Western ears, accustomed as we are to a divide between reason and affections. However, such a love that overflows in knowledge could transform much of our politics.
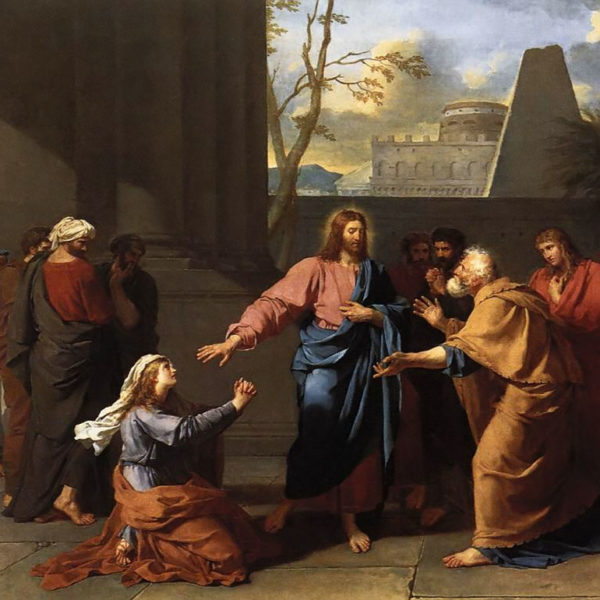

In turning Jesus’ seemingly dismissive image of dogs and children at the meal table to her advantage, the Syrophoenician woman illustrates the tenacity of parents fighting for their children. As we act in God’s name within the world we should show the same determination on behalf of all of his children.
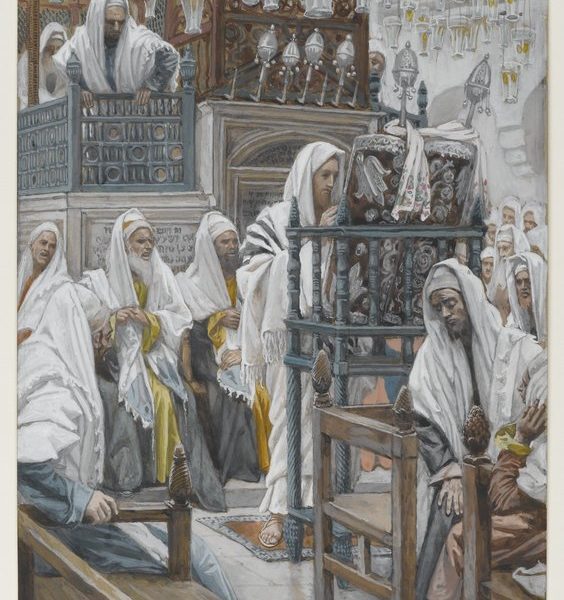

In this week’s reading from Mark’s gospel Jesus challenges the complacency that so commonly comes with privilege. The ease of privilege within the status quo can inure us to the claims of truth or justice that might unsettle it or that might trouble its assurance of its purchase upon reality. Yet such claims lie at the very heart of the Kingdom of God.
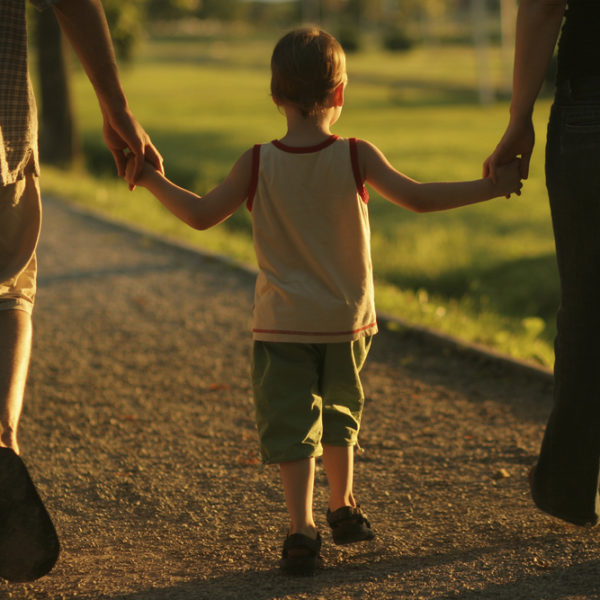

Our discomfort with the notion of God visiting the sins of parents upon their children may lead us to avoid wrestling with Exodus 20:5-6. This would be a mistake. This reference occurs in the context of the prohibition upon idolatry and challenges both our attempts to sanitize God and our idolization of our children.
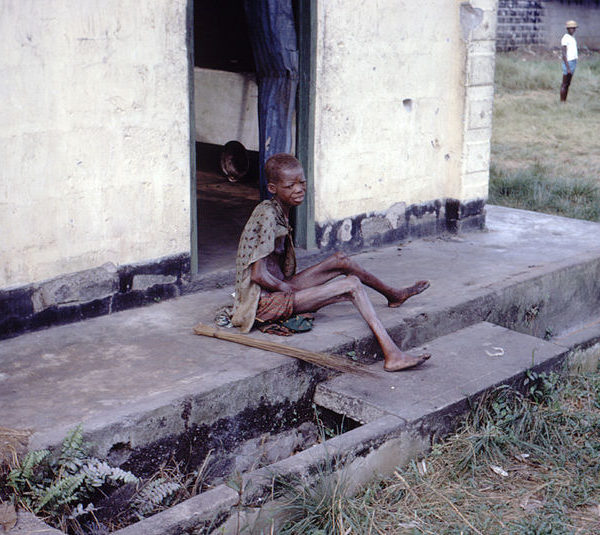

Perhaps part of the reason why disparities in food distribution continue to exist is that, when those of us who have food enough on our tables try to respond to disasters such as famine, without connection with the people who suffer them, both they and us are likely to come away empty. The ironic use of famine in Naomi’s story is able to suggest to us another way, an approach to famine that sees first the emptiness in relationships when kin from the ‘developing’ and ‘developed’ worlds find ourselves absent from one another.
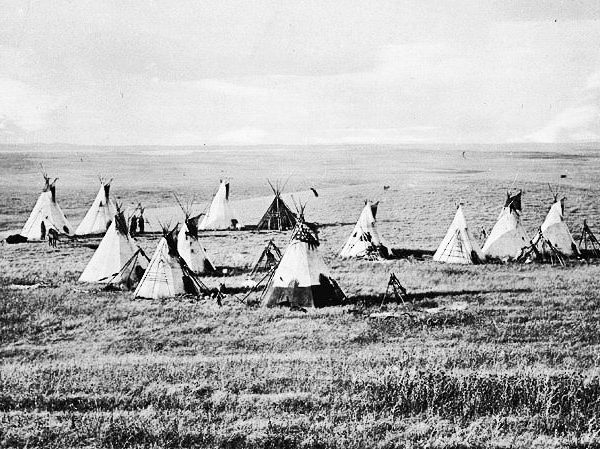

Exodus reminds us of what as human beings we have in common with the land and all of its resources—we are all both creations and possessions of the eternal God. In light of this, as we recognize and respond to our own needs and desires, making claims on the land as a result, we must also recognize the land as possessing its own distinct claims, dignity, and integrity.
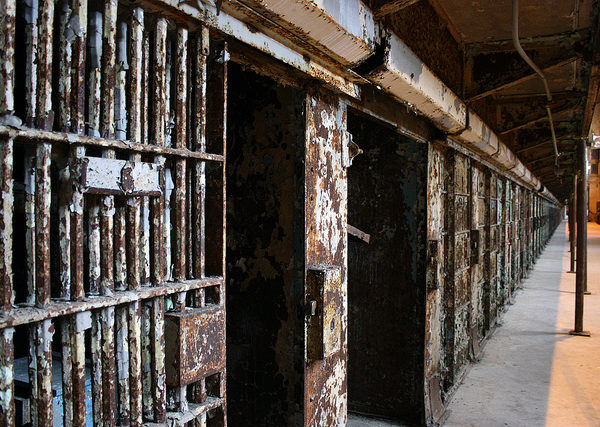

In the account of the slave with the spirit of divination, Paul, Silas, the Philippian jailer, and his family we encounter dynamics of agency and constraint, of freedom and slavery. There are a number of surprising instances of human action within this narrative which nonetheless speaks powerfully of the power and activity of God.
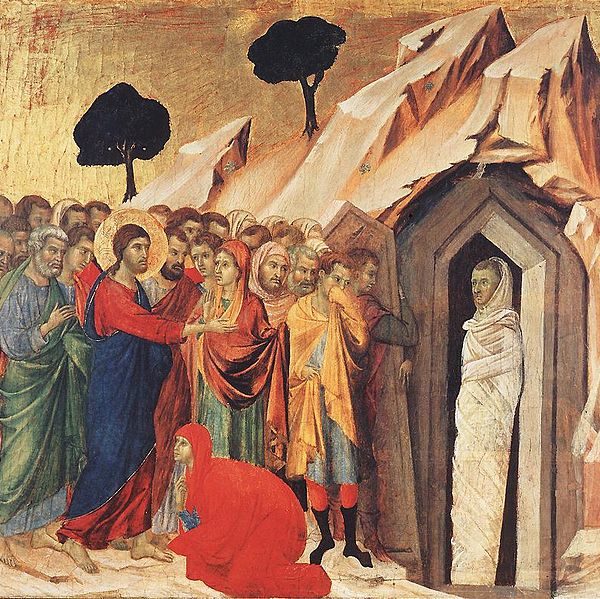

Although at first glance they may appear incidental, the frequency of border crossings in the story of the raising of Lazarus suggests the presence of a theme. Through a narrative of successive boundary crossings, the power and willingness of God to traverse any distance and border is made manifest.
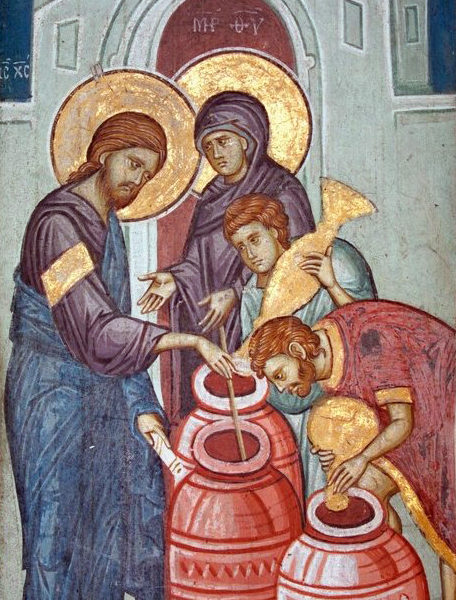

In John’s account of the Wedding of Cana, the part played by Mary merits our attention. On account of the honor due to her as a mother, she wields great authority. She provides us with occasion to reflect upon the esteem in which we hold mothers today and the authority that we accord them in our lives and society.

In light of the two kingdoms doctrine and the separation of church and state, understanding the appropriate form of Christian prayer for and engagement with the political realities of our societies can be complex. In Jeremiah’s message to an exiled people, we find a pattern for prayer in a pluralistic context, a calling that identifies our primary task to be one of seeking the common good and welfare of our communities, rather than one of submission or conversion.