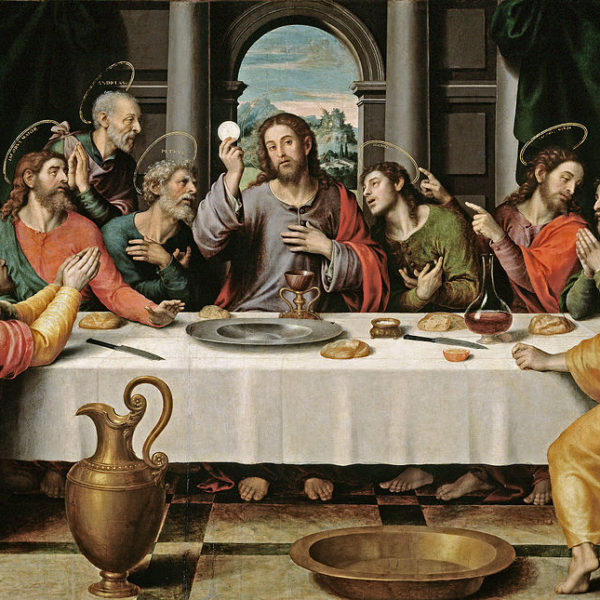
In celebrating the Eucharist, we are engaging in an act of remembering those who were remembering those who were remembering. To remember is to ‘re-member’, to re-attach ourselves to the great story of God’s deliverance.
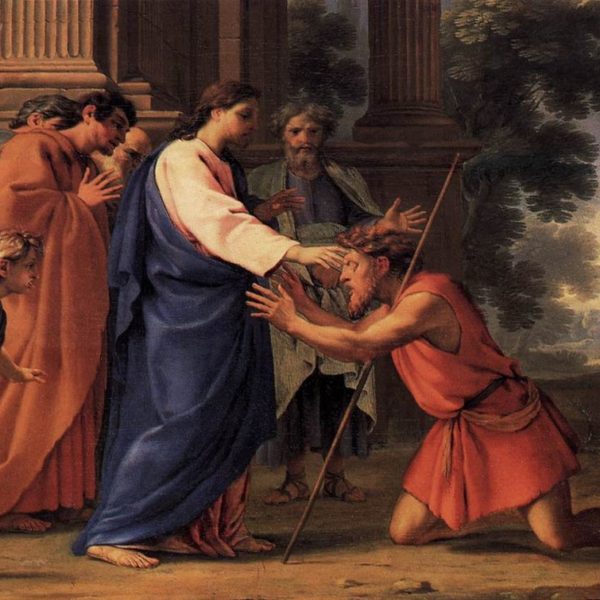

In the healing of the blind man in John 9 and the response of the religious leaders and teachers that follows, the power of scapegoating is revealed, as is the assurance that Jesus will overcome it.
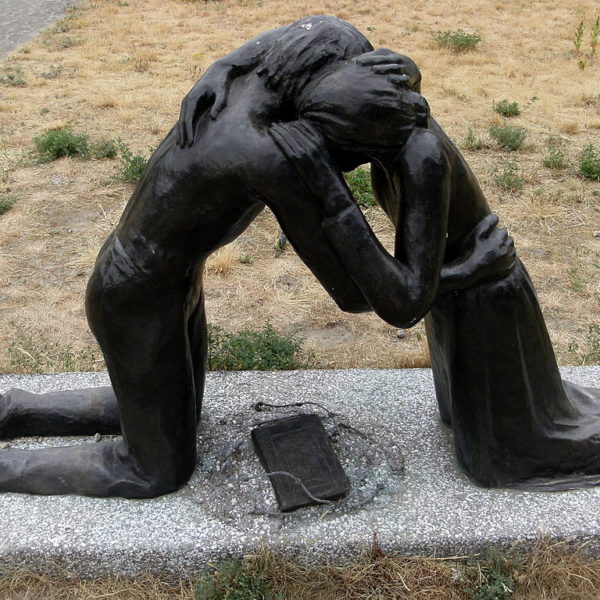

In Romans, Paul speaks of a God of reconciliation, who makes friends of enemies. Principles of reconciliation and of the love of enemies have often been quarantined from the political realm in systems of political thought that prioritize the enemy-friend polarity. However, a politics of love for enemies and of reconciliation with a creation from which we have become alienated may never have been more urgent.