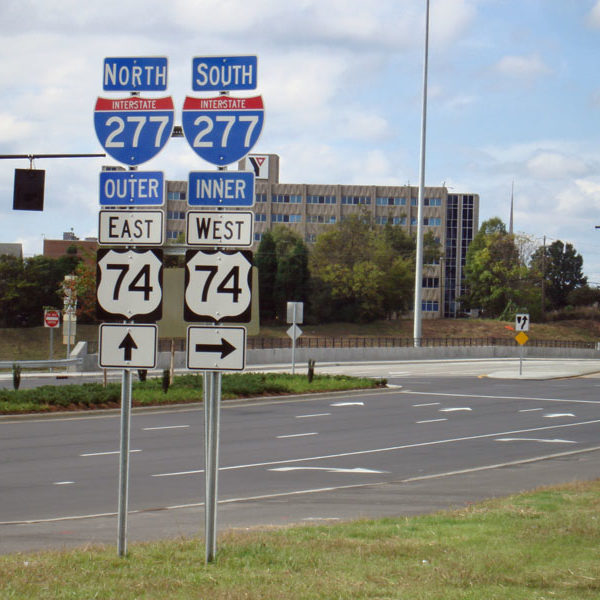
Mt. Carmel represents a very particular vision of Divine power, one dependent on a definition of power that equates it entirely with the strength to impose one’s will on another – even to the point of death. It’s an astonishing demonstration, yet also an extremist one, requiring power to equal unfathomable force: the unquenchable fire and Elijah’s subsequent unquenchable thirst to eliminate his enemies.

The text of 1 Kings 8 is a conversation, not a monologue. For those of us who look to Scripture to guide our understanding and action in our own context, this text invites us to wrestle, conversationally, with the embedded ideologies of our own political leaders’ projects. Names matter in politics. But humble leadership, for the good of all, ought to matter more.

In our zeal for the projects to which we commit ourselves, especially when we see them as responding to God’s call upon our lives, we risk a myopia that obscures our perception of other realities. Elijah’s story serves as both a warning and a source of hope to those of us inclined to abandon the institutional church, reminding us that there are likely many others who share our deepest commitments, even if these others remain invisible to us for now.

Jezebel embraces her gods just as Elijah does. When the prophets of her gods are mocked and killed in a most disrespectful way, Jezebel is angered. In the face of death, she remains fearless. Her fearlessness combined with her reverence to her gods in a foreign land makes her an example for contemporary women.

Framed merely as a story about the call to discipleship, and omitting verses 17-18, the fact that God is instigating political coups through his prophets in this passage could easily be missed if we didn’t consider the scriptural context of this week’s lectionary reading. Reflecting upon this passage and the ensuing events, we can learn something about God’s relationship to political rule.

According to 1 Kings 8, prayer is what Israel is supposed to do in times of helpless hopelessness. The temple is where they turn when there is nowhere to turn. Israel as a whole was invited to appeal to the High King for help in times of trial, and the text leads us to wonder if every polity directs its hopes toward a temple.

Elijah’s ministry takes place during the reign of king Ahab in the 9th century BC. The narrative about the prophet is expressly political. It depicts a political dissident who speaks against the powers of his day, with the main focus on promoting the worship of Yahweh and fighting against the worship of Baal. The prophet’s actions must be understood against a wider Near Eastern context where religion was completely intertwined with politics and where Yahweh was the national god of the Israelites.