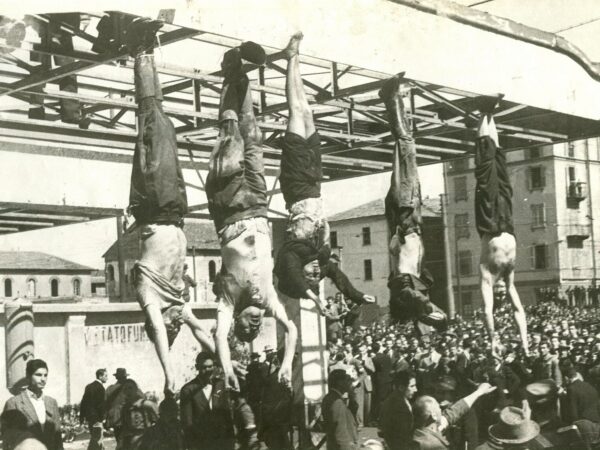
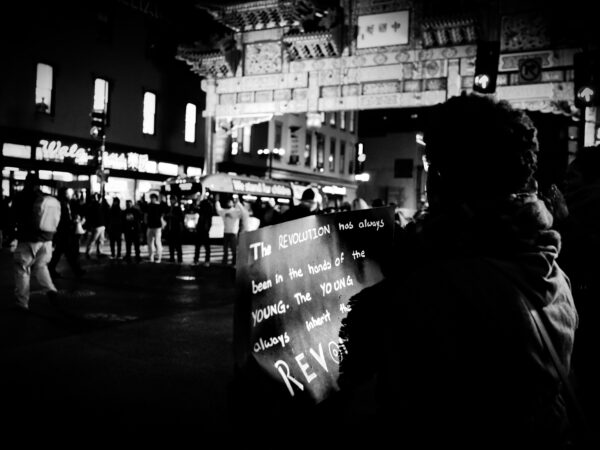
To undertake the reformation of desires is a calling, with no guarantees of success, but some promise of God’s grace along the way.

What is the role of atheism in bringing hope to troubled times? Controversially, I/Stacey stress(es) that atheism too often reproduces the transcendence it claims to reject. Instead, bringing insights from my/his time among activists, I/he argue(s) that a good atheism must be in touch with immanence.

Liberation, caught between queer nihilism and eschatological certainty, must seek an third way beyond the binary of hopefulness and hopelessness through the negation of both. It must transpose itself into an apophatic register as the experience of continual failure, an uncertain endless becoming, that might be called simple hope.

As literary works of speculative fiction, Octavia Butler’s Parable of the Sower (1993) and Parable of the Talents (1998) thrust us into an all-too-near future, offering a haunting perspective on what our world could entail by the year 2035. In 2024, however, Butler’s Parables are no longer mere imaginative forays into the future.

The journal Political Theology will host an open house on February 1 at noon eastern for prospective authors and contributors to the journal.

From the perspective of political theology, the presence of Indigenous peoples and settlers shaped by historical and ongoing settler colonial relations raises important political and religious questions about the possibilities and conditions of sovereign Indigenous existence and the (im)possibities and conditions of restorative or reconciled settler futures.

Christian nationalism is a form of superstition. It is superstitious because, instead of appealing to the God of all nations, it appeals to a culturally fabricated God for cultural privilege, power, and benefits.

Khilafat in the narratives during the rebellion represented freedom, dignity, justice and universal brotherhood instead of the restoration of an empire. The article briefly examines multiple possibilities the term Khilafat or Caliphate offered to the indigenous anti-colonial struggle of Malabar in India in the 20th century.