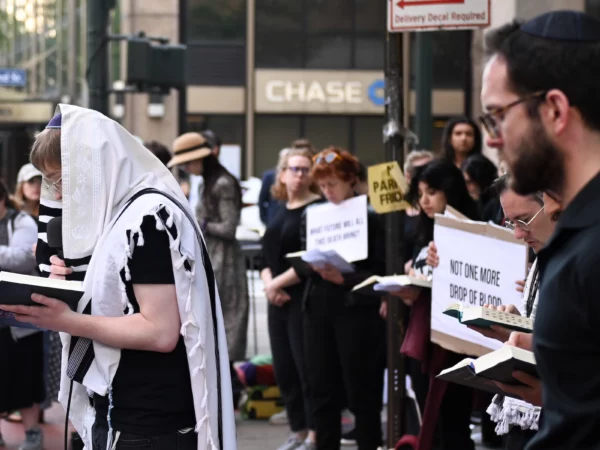
The grass seemed greener in Orthodoxy, I’ve realized, because my yearning for authenticity and escape reflected a structural lack embedded in late capitalist dystopia… Today, it seems to me more honest to learn to live with this lack, than to imagine that any faith, flag or folkway can fully fill it.
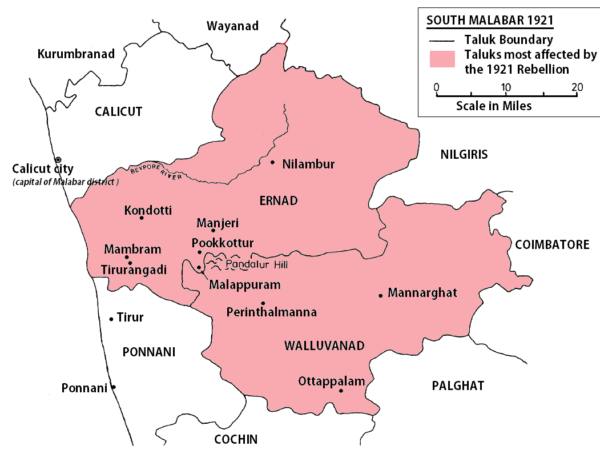
This blog post investigates and problematizes a certain narrative strategy in the historiography of Malabar rebellion, in which “war” (“yudham”) and “riot” (“lahala” or “mutiny”) were configured on the model of “politics” and “religion”. The post asks what kind of sovereign formation was imagined in such a narrative strategy and why it needs to be addressed.

From Myanmar to Mariupol, from the streets of Memphis to the waves and winds of the Mediterranean Sea: resistance to violence takes many forms. So does political protest against precarity. At which point does the unavoidable vulnerability of the living condition come to expression as political agency? Can such precarious politics constitute or configure an alternative community?

What is still nascent… is an explicit conversation between political theology and critical theories of affect, particularly in a way that might contribute to constructive projects. The sort of political theology that might emerge from such collaboration would consider how affective regimes intersect with theological constructions or religious performances.







