After half a dozen years of economic decline and political hardship EU measured its demos in the elections to the European Parliament. The result was just about expected, though probably not at all what the ”Europeans” — whoever they are these days — were eager to see. Given a choice between a commitment towards the globalization of world politics and going home, going home, by and large, won.

I want to argue here that the term “political Islam” is in many ways a misnomer, because the Islamism that is meant to instantiate it has been unable to appropriate politics as a way of dealing with antagonism either institutionally or even in the realm of thought. Looking in particular at the form Islamism took with one of its founding figures, the twentieth century writer, and founder of the Jamaat-e Islami in both India and Pakistan, Sayyid Abul a’la Maududi.

In Simon Critchley’s Wildean confraternity or consorority of the faithless, faith is a commitment, a proclamation of fidelity to an infinite ethical demand which enacts a new form of subjectivity. As such, faith is not related to belief in the existence of God but to an experience that is shared by agnostics, atheists and theists alike. Faith, we might say, is a/theistic, cutting across such distinctions.
If my diagnosis of the situation above is apt, it seems that Christian participation in domestic politics today may also be a matter for deferred repentance.

As we reflect on what it means to resist vulnerability and consolidate military power, much could be said in connection to our own political moment. Given the proliferation of weapons of war and the investment in such weaponry by nation-states and stakeholders who see buying shares in war-related machinery and technology as a profitable enterprise, the privileging of a good heart—“the LORD looks on the heart”—is a most urgent political posture.
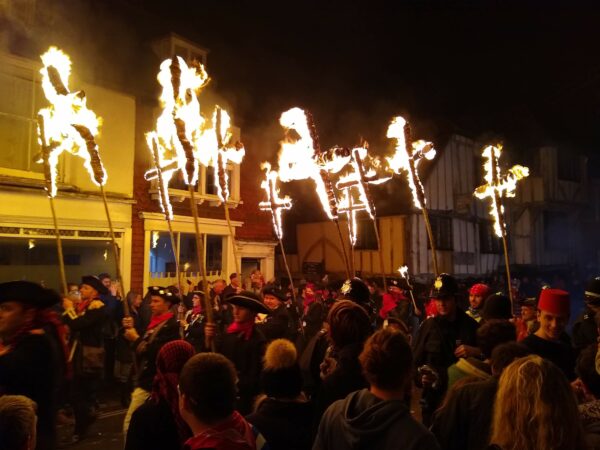

The modern state form itself is inextricable from the commandement, not just as an emblem for sovereignty in Schmitt’s sense, but also because the exemplary political form of modernity, the nation-state, has racist and exclusionary tendencies that can be understood as political-theological transfers of monotheistic principles.
This symposium celebrates George Shulman’s work on political theology by continuing the conversation that formally concluded when Shulman’s “Political Theology” seminar met for the last time in the spring of 2021.

For Muslims to become worthy of any empathy and solidarity, whether in the west or in staunchly anti-Muslim India, what must first be shed is our very religiosity. Islam is to be tolerated only when reduced to culture in which the dominant-caste or white friend can joyously celebrate Muslim festivities, visit Muslim friends and restaurants for biryani in Toronto or Delhi, or post Sufi songs on their social media. Those are the parameters set around reception of a Muslim sans Islam.


